What is Site Investigation?
Site investigation is the process of gathering information about the physical characteristics of a construction site to ensure its suitability for a project. Whether it’s a residential development, commercial building, or infrastructure project, site investigation helps determine the ground conditions and identify any potential risks. This includes the study of soil and rock properties, groundwater conditions, and environmental factors that could affect construction. By conducting thorough investigations, developers can minimize delays, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Understanding the importance of site investigation is crucial because it helps developers avoid the costly consequences of unforeseen ground conditions. Without a proper site investigation, a project might face delays due to soil instability, contamination, or other hidden issues. It also helps to streamline environmental compliance processes, ensuring that all legal and regulatory obligations are met.
Why is Site Investigation Important?
The significance of site investigation lies in its ability to prevent potential problems during construction. Unforeseen issues such as unsuitable soil conditions, groundwater levels, and contamination can all lead to costly delays and even project failures. A comprehensive site investigation allows construction managers to design foundations, drainage systems, and structures that are safe, efficient, and compliant with regulations.
Key reasons why site investigation is essential include:
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying soil conditions, groundwater levels, and contamination risks, developers can avoid unexpected problems that could delay construction or increase costs.
- Cost Savings: Site investigation helps to accurately assess the soil and rock properties, allowing for proper planning and design. This avoids expensive redesigns and over-engineering of foundations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Environmental and geotechnical regulations in Australia often require a detailed site investigation to ensure that the project does not cause undue harm to the environment or pose risks to future occupants.
Without a thorough site investigation, project managers may face expensive fines, legal challenges, and potential reputational damage if issues such as contaminated soil are discovered later in the process.
Types of Site Investigations
The type and extent of site investigation depend on the complexity of the construction project and the risks associated with the site. There are three primary types of site investigations:
- Preliminary Site Investigation (PSI): This is an initial survey designed to gather background information on the site. It typically involves reviewing previous records, geological maps, and existing data about the location. The goal is to determine if more detailed investigations are required.
- Detailed Site Investigation (DSI): A more comprehensive approach, the detailed investigation involves conducting field and laboratory tests to determine the subsurface conditions. Techniques such as test borings and soil sampling are used to gather data on soil stability, rock characteristics, and groundwater levels.
- Supplementary Investigation: This type of investigation is often conducted if unexpected issues arise during the construction phase, such as encountering contaminated soil or unstable ground. A supplementary investigation allows for additional analysis to ensure that the project remains on track.
Each type of investigation serves a specific purpose, but they all share the goal of identifying potential risks and providing data that will inform the construction design and planning process.
The Site Investigation Process
The site investigation process involves multiple steps to ensure that the necessary data is gathered, analyzed, and used effectively. A typical site investigation includes the following stages:
- Planning and Desk Study: Before any physical tests are conducted, project managers review existing records about the site, such as maps, historical data, and prior investigations. This helps to determine the scope of the investigation and identify any known issues, such as contaminated land.
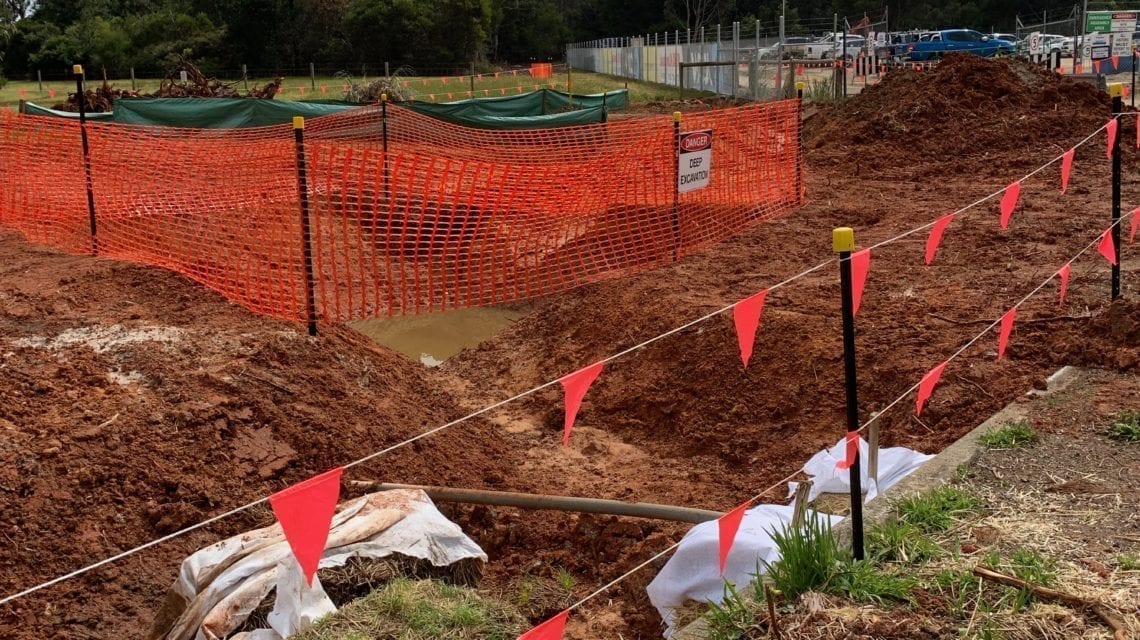
- Fieldwork and Data Collection: The actual investigation begins with on-site activities such as drilling boreholes, taking soil samples, and conducting field tests. This stage may also involve geophysical surveys and groundwater monitoring.
- Laboratory Tests: Once soil and rock samples are collected, they are analyzed in the lab to determine their properties, including strength, permeability, and chemical composition. This step is critical for identifying whether the site is suitable for construction and determining any necessary remediation measures.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: After the data is collected and analyzed, geotechnical engineers prepare a detailed report. This report includes findings about the soil condition, groundwater levels, and any environmental hazards, as well as recommendations for construction methods and risk mitigation.
The site investigation process is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the site, ensuring that construction can proceed with minimal risk of unexpected complications.
Essential Tools and Techniques
A wide range of tools and techniques are employed during site investigations to gather the necessary data about the subsurface conditions. These include both fieldwork and laboratory tests, all of which are critical for understanding the soil and rock properties.
- Test Borings: One of the most common methods, test borings involve drilling into the ground to collect samples of soil and rock. This allows engineers to examine the stratification of the soil layers and assess their suitability for supporting structures.
Dynamic Cone Penetrometer (DCP): This tool is used to determine the strength and stiffness of soil at shallow depths. It is a cost-effective method for assessing the stability of the ground before construction begins.
- Soil Sampling: By collecting soil samples from various depths, engineers can analyze their physical and chemical properties. Laboratory tests can then provide valuable information about the soil’s composition, strength, and any potential contamination.
- Geophysical Surveys: Techniques such as seismic reflection and ground-penetrating radar (GPR) are used to create detailed images of the subsurface. These methods are particularly useful for identifying features such as buried utilities, groundwater, and faults in the rock.
- Laboratory Tests: Once the samples are collected, they are subjected to a series of tests to determine their mechanical and chemical properties. This includes assessing the strength of the soil, its permeability, and its ability to support structures. Laboratory tests are essential for understanding how the ground will behave under load.
By utilizing these tools and techniques, site investigations provide the data needed to design safe and efficient foundations, drainage systems, and other critical infrastructure components.
Challenges and Considerations
Site investigations are not without their challenges. Developers and geotechnical engineers must consider several factors to ensure a successful investigation and subsequent construction. Some common challenges include:
- Access to Remote or Urban Sites: Some sites, particularly those in remote areas or dense urban environments, can be difficult to access with large equipment. This may require creative solutions, such as using portable equipment or conducting investigations during off-peak hours.
- Unfavorable Weather Conditions: In Australia, weather conditions such as heavy rains, floods, or extreme heat can hinder fieldwork. It is important to plan the investigation around seasonal weather patterns to avoid delays.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Certain construction sites, particularly those near protected natural areas, may require special considerations to minimize environmental impact. This could include using non-invasive testing methods or ensuring that any contaminated soil is handled and disposed of properly.
- Regulatory Requirements: Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations is a key consideration for any site investigation. Failing to meet these requirements can result in fines, delays, or even the halting of the construction project.
By addressing these challenges proactively, developers can ensure that their site investigations are both efficient and effective.
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
In Australia, site investigations must adhere to a range of legal and regulatory requirements to ensure both environmental protection and public safety. Some of the most important regulations include:
- Australian Standard AS 1726 Geotechnical Site Investigations: This standard outlines the procedures for conducting site investigations, including the methods for soil sampling, test borings, and laboratory analysis. Compliance with this standard ensures that the investigation is conducted safely and effectively.
- Environmental Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act: Projects that may impact the environment, particularly those in sensitive areas, must comply with this federal legislation. It requires that any environmental risks are identified and mitigated through thorough site investigations.
- State-Based Regulations: Each state in Australia has additional requirements for site investigations, particularly when it comes to contaminated land and groundwater management. These regulations are designed to protect public health and ensure the safety of construction projects.
By staying compliant with these regulations, developers can avoid legal challenges and ensure that their projects proceed smoothly.
A comprehensive site investigation is a vital step in ensuring the success of any construction project. By understanding the subsurface conditions, developers can avoid costly delays, reduce risks, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Whether it’s a preliminary investigation or a detailed assessment involving test borings and laboratory tests, the insights gained from site investigation are essential for the safe and efficient execution of a project.
Looking for reliable environmental consultants? iEnvironmental Australia offers expert site investigation services, tailored to meet the needs of your project. Contact us today to ensure that your next construction project is built on a solid foundation.


 Dynamic Cone Penetrometer (DCP): This tool is used to determine the strength and stiffness of soil at shallow depths. It is a cost-effective method for assessing the stability of the ground before construction begins.
Dynamic Cone Penetrometer (DCP): This tool is used to determine the strength and stiffness of soil at shallow depths. It is a cost-effective method for assessing the stability of the ground before construction begins.